Program
Recently, researcher He Xianqiang of the SIO and the co-authors published the research paper entitled “Atmospheric correction of absorbing aerosols for satellite ocean color remote sensing over coastal waters” in Remote Sensing of Environment (IF=13.8), a top international journal in remote sensing. The first author of the paper is Song Zigeng, a doctoral candidate jointly trained by the SIO and Hohai University, and the corresponding author is researcher He Xianqiang of the SIO. The co-authors include researcher Bai Yan, researcher Wang Difeng, associate researcher Li Teng, professor level senior engineer Zhu Qiankun and senior engineer Gong Fang from the SIO, and associate professor Dong Xinyi of Nanjing University.
The atmospheric correction (AC) of ocean color remote sensing is greatly affected by the vertical distribution of absorbing aerosols (AA), especially for remote sensing reflectance (Rrs(λ)) retrievals in the blue and ultraviolet bands. In the early stage, we constructed the AA vertical distribution retrieval model (Song, He*, et al., 2020) and the AA optical property model (Song, He*, et al., 2022), which can quantitatively retrieve the vertical height of AA, and simulated the TOA reflectance (ρt(λ)) and remote sensing reflectance (Rrs(λ)) in the presence of AA by air-sea coupled radiative transport model. On this basis, a new AC algorithm (OC-XGBRT), which is based on extensive radiative simulation and machine learning model, was developed to retrieve the Rrs(λ) at the blue bands to reduce the influence of AA while considering its vertical distribution. The algorithm flow chart is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1 Flow chart of OC-XGBRT algorithm
The goal of OC-XGBRT algorithm is to improve the data quality of Rrs(λ) in coastal waters under the influence of AA. In this study, the OC-XGBRT algorithm is applied to the MODIS-Aqua water color sensor, verified by SeaBASS and AERONET-OC measured site data, and compared with NASA SeaDAS, POLYMER and OC-SMART AC algorithm. The verification results of Rrs(412 nm), Rrs(443 nm), Rrs(488 nm) and Rrs(547 nm) are shown in Figure 2. The mean absolute percentage deviation (APD) and root mean square error (RMSE) values of OC-XGBRT are less than 36.9% and 5.5 ×10-4 sr-1, respectively, showing that OC-XGBRT can provide more accurate remote sensing reflectance products in coastal and inland waters.
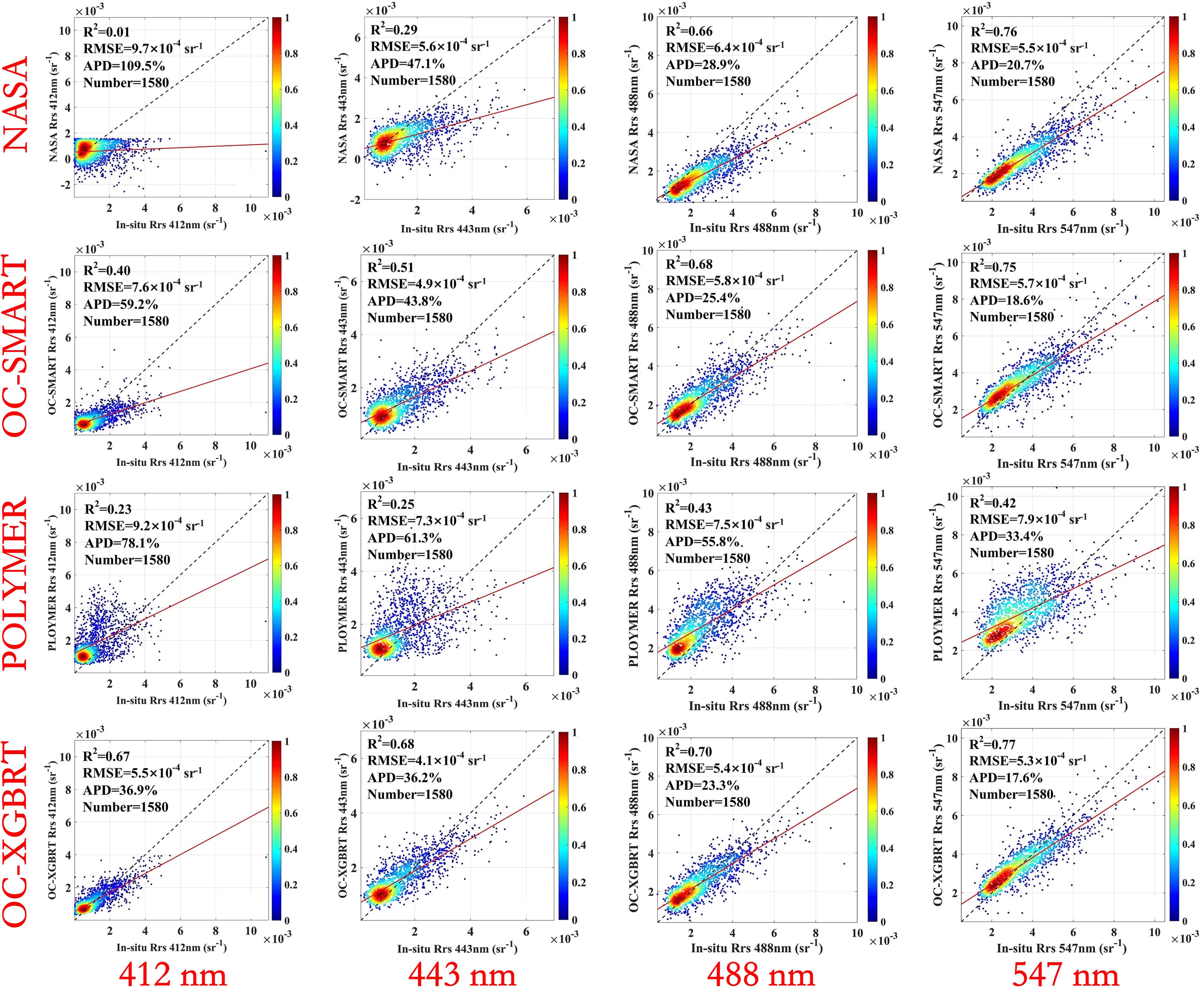
Figure 2 Comparative validation of Rrs (412 nm), Rrs (443 nm), Rrs (488 nm) and Rrs (547 nm) retrieved by NASA SeaDAS, PLOYMER, OC-SMART and OC-XGBRT in SeaBASS and AERONET-OC measured values in the presence of AA.
In this study, six typical offshore areas (West African coast, Persian Gulf, East and West Coast of America, Black Sea, the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea of China) were selected for quantitative assessment. Figure 3 shows the results of the Persian Gulf. The correction results of OC-XGBRT are significantly improved compared with NASA products, and Rrs(412 nm) and Rrs(443 nm) are no longer negative and are close to the measured values. Application results of OC-XGBRT in six typical regions further demonstrated that the quality of retrieved Rrs(412 nm) and Rrs(443 nm) had substantially improved compared with NASA products under the condition of AA. Moreover, the implementation of the OC-XGBRT algorithm contributes to a significant enhancement in the spatial coverage of utilizable Rrs(λ) values at blue bands. The OC-XGBRT AC algorithm has the potential to process ocean color satellite data under the condition of AA.

Figure 3 (a) MODIS-Aqua RGB image obtained over the Persian Gulf on December 10, 2007 (10:05 UTC); (b) NASA Rrs(412 nm) product (unit sr-1); (c) NASA Rrs(443 nm) product; (d) Aerosol type; (e) AOD(412 nm); (f) Rrs(412 nm) retrieved by OC-XGBRT; (g) Rrs(443 nm) retrieved by OC-XGBRT; (h) Quantitative comparison of MODIS-Aqua Rrs(λ) spectra retrieved by NASA products, OC-SMART and OC-XGBRT algorithms with field measurements. DU, SM, UR, and NWA represent dust, smoke, urban type, and non or weakly absorbing aerosol, respectively.
Paper Citation:
Song, Z., He, X.*, Bai, Y., Dong, X., Wang, D., Li, T., Zhu, Q., & Gong, F. (2023). Atmospheric correction of absorbing aerosols for satellite ocean color remote sensing over coastal waters. Remote Sensing of Environment, 290, 113552.



